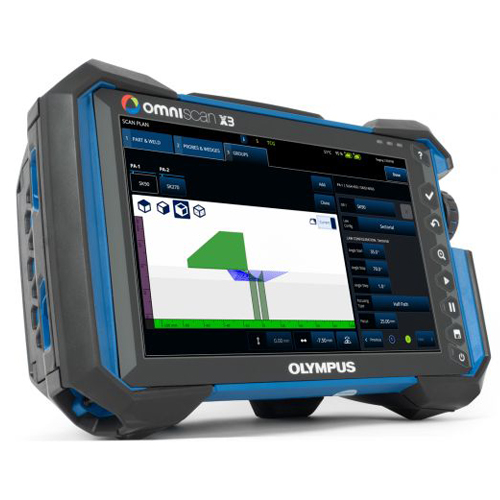
Olympus OmniScan X3 Phased Array Flaw Detector is an advanced, versatile, and user-friendly ultrasonic testing instrument for Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) applications.
The Olympus OmniScan X3 Phased Array Flaw Detector was introduced and released by Olympus Corporation in October 2019, building upon the success and features of its predecessors in the OmniScan product line.
Package includes:
– OmniScan X3 flaw detector
– Li-ion battery (1)
– Anti glare screen protector (1)
– DC power adaptor
– Power cord
– Microfiber cloths
– USB key (16 GB)
– Wireless LAN dongle
– USB flash drive (key), which contains : Instrument software
– OmniScan X3 Getting Started Guide
– OmniScan X3 User’s Manual
– OmniScan MXU Software User’s Manual
– Warranty card
– Travel Case
OmniScan X3 Flaw Detector Redefines the Standard for Phased Array
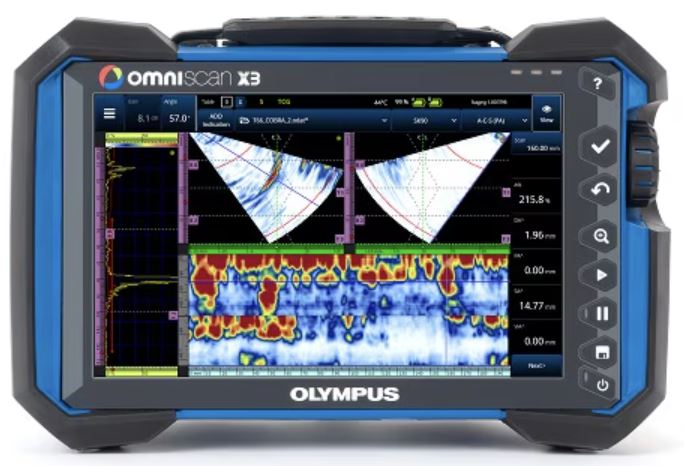 OmniScan instruments are recognized globally as the benchmark for portable phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT) thanks to their power, reliability and ease of use. The new OmniScan X3 flaw detector elevates the standard with innovations that improve the entire inspection workflow. Setting up for a job is faster and more efficient while total focusing method (TFM) images collected through full matrix capture (FMC) give users more confidence in their decision making. When an inspection is complete, leading-edge software tools make analysis and reporting easier.
OmniScan instruments are recognized globally as the benchmark for portable phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT) thanks to their power, reliability and ease of use. The new OmniScan X3 flaw detector elevates the standard with innovations that improve the entire inspection workflow. Setting up for a job is faster and more efficient while total focusing method (TFM) images collected through full matrix capture (FMC) give users more confidence in their decision making. When an inspection is complete, leading-edge software tools make analysis and reporting easier.
The OmniScan X3 flaw detector combines the essential tools needed for PAUT inspections, such as TOFD, two UT channels, eight groups and 16:64PR, 16:128PR and 32:128PR configurations*, with powerful innovations, including:
- TFM/FMC with 64-element aperture support
- Improved phased array imaging, including an innovative live TFM envelope feature
- Acoustic influence map (AIM) simulator for TFM mode
- 25 GB file size
- Up to 1,024 × 1,024-pixel TFM reconstruction and four simultaneous, live TFM propagation modes
- Simplified user interface with onboard scan plan
- Wireless connectivity to the Olympus Scientific Cloud (OSC) makes it simple to keep the instrument’s software up to date.
The comprehensive onboard scan plan tool enables users to visualize the inspection, helping reduce the risk of errors. The entire scan plan, including the TFM zone, can be created in one simple workflow. Creating a setup is also faster with improved calibration tools and support for simultaneous probe and beam set configuration, onboard dual linear, matrix and dual matrix array creation and automatic wedge verification.
Certified IP65 dust proof and water resistant, the instrument has the reliability and ease of use that OmniScan flaw detectors are known for combined with high-quality images that help make interpreting flaws more obvious. With the total focusing method, users can produce geometrically correct images to confirm the characterization of flaws identified through conventional phased array techniques and obtain better images throughout the volume of a part. Additional features that enable outstanding images include a 16-bit A-scan, interpolation and smoothing and a vivid 10.6-inch WXGA display that provides clarity and visibility in any light.
The OmniScan X3 flaw detector makes analysis and reporting faster, both onboard the instrument and on a PC. The instrument also comes with a variety of helpful data interpretation tools: Circumferential outside diameter (COD) TFM image reconstruction to facilitate interpretation and sizing of long seam weld indications Merged B-scan to facilitate the screening of phased array weld indications while keeping the workflow simple
Whether inspecting pipes, welds, pressure vessels or composites, the OmniScan X3 flaw detector enables users to complete their work efficiently and interpret flaws with confidence.
The OmniScan X3 flaw detector has the tools to help you complete your work efficiently. Its range of applications include welds, pipelines, pipes, corrosion-resistant alloys, corrosion mapping, HTHA inspection, detection of stepwise cracking, composite inspection, and flaw imaging.
– Compatible with existing probes and scanners
– 32:128PR model, featuring 64-element TFM
– 16:64PR and 16:128PR also available
– Up to 8 groups, 1,024 focal laws
– Compatible with MX2/SX files for convenience
– 64 GB internal storage, extendable with an external USB drive
Features:
– Powerful software that’s intuitive for new and existing OmniScan users with a modern, simplified menu structure that minimizes button presses.
– Live TFM Envelope Processing. The instrument’s unique envelope processing provides clear, high-resolution TFM images of flaws.
– Facilitate Flaw Interpretation and Sizing. Using different TFM modes (wave sets) in the same inspection provides more chances to detect oddly oriented indications.
– Confirm Your Coverage in Advance. The acoustic influence map (AIM) tool provides you with an instant visual model of the sensitivity based on your TFM mode, probe, settings, and simulated reflector.
– Get to Work, quickly. The onboard scan plan tool helps you visualize your inspection before you begin.
– Improved Fast Calibration. The OmniScan X3 calibration menus track the signals at high speed. You can perform multiple group calibrations in minutes with minimal frustration
– Harness the Power of Your PC. OmniPC™ software offers a suite of advanced tools, such as a side-by-side view that enables you to compare two files onscreen at the same time to maximize the power of your PC when analyzing data.
Olympus OmniScan X3 Phased Array Flaw Detector Applications:
– In-service and construction welding
– Pressure vessels
– Process pipes
– Wind tower
– Structural construction
– Corrosion-resistant alloys and cladded materials (austenitic, nickel, and other coarse-grained materials)
Olympus OmniScan X3 Phased Array Flaw Detector Specifications:
| Type | Multigroup, multimode ultrasonic flaw detector |
| Size (W × H × D) | 335 mm x 221 mm x 151 mm (13.2 in. x 8.7 in. x 5.9 in.) |
| Weight | 5.7 kg (12.6 lb) (with 1 battery) |
| Hard Drive Capacity | OmniScan X3 : Internal 64 GB SSD OmniScan X3 64 : Internal 1TB SSD extendable using an external USB drive |
| Storage Devices | SDHC™ and SDXC™ cards or most standard USB storage devices Compatible only with NTFS and FAT32 formats. |
| Max Onboard File Size | 25 GB |
| GPS | Yes (unless specified otherwise for some regions) |
| Alarms | 3 |
| Wireless Connection | Yes – wireless LAN dongle included in the package (model varies according to region) |
| PA Connectors | 1 connector |
| UT Connectors | 4 (2 channels P/R) |
| Certifications | ISO 18563-1:2015 ISO-22232-1:2020 |
| Display | |
| Type | TFT LCD with resistive touch screen |
| Size | 269 mm (10.6 in.) |
| Resolution | 1280 × 768 pixels |
| Number of Colors | 16 million |
| Viewing Angles | Horizontal: −85° to 85° Vertical: −85° to 85° |
| I/O Ports | |
| USB 2.0 | 2 ports (one hidden behind the battery) |
| USB 3.0 | 1 port |
| Video Output | Video out (HDMI) |
| Memory Card | SDHC port |
| Communication | Ethernet |
| I/O Lines | |
| Encoder | 2-axis encoder line (quadrature quadrature direction) |
| Digital Input | 6 digital inputs, TTL |
| Digital Output | 5 digital outputs, TTL |
| Acquisition On/Off Switch | Through the configuration of a digital input |
| Power Output Line | 5 V nominal, 1 A (short-circuit protected), and 12 V output at 1 A |
| External DC Supply | |
| DC-IN Voltage | 15 VDC to 18 VDC (min. 50 W) |
| Connector | Circular, 2.5 mm pin diameter, center-positive |
| Battery | |
| Type | Lithium-ion battery |
| Capacity | 87 Wh |
| Number of Batteries | 2 |
| Life | 5 hours using 2 batteries (hot-swap capable) |
| PA/UT Configuration | |
| Bit Depth | 16 bits |
| Maximum PRF | 20 kHz |
| Frequency | |
| Effective Digitizing Frequency | Up to 100 MHz |
| Display | |
| Refresh Rate | A-scan: 60 Hz; S-scan: 20 Hz to 30 Hz |
| Envelope (echo-dynamic mode) | Yes: Volume-corrected S-scan (30 Hz) |
| A-Scan Height | Up to 800% |
| Synchronization | |
| On Internal Clock | 1 Hz to 10 kHz |
| External Pace | Yes |
| On Encoder | On 2 axes: from 1 to 65,536 steps |
Data Specifications
| Processing | |
| Maximum Number of A-Scan Data Points | Up to 16,384 |
| Real-Time Averaging | PA: 2, 4, 8, 16 UT: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 |
| Rectification | RF, full wave, half wave+, half wave- |
| Filtering | PA channel (OmniScan X3): 8 low-pass, 6 band-pass, and 4 high-pass filters PA channel (OmniScan X3 64): 9 band-pass and 7 high-pass filters UT channel: 8 low-pass, 6 band-pass, and 4 high- pass filters (3 additional filters when configured in TOFD) |
| Video Filtering | Smoothing (adjusted to the probe frequency range) |
| Programmable TCG | |
| Number of Points | 32: One TCG (time-corrected gain) curve per focal law |
| Range | PA (standard): 40 dB per step of 0.1 dB UT: 100 dB per step of 0.1 dB |
| Maximum Slope | PA (standard): 40 dB/10 ns UT: 40 dB/10 ns |
Acoustic Specifications
| Model | OmniScan X3 | OmniScan X3 64 | Both |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulser | PA Channel | PA Channel | UT Channels |
| Voltage | 40 V, 80 V, and 115 V | 10 Vpp, 20 Vpp, 40 Vpp, 80 Vpp, 120 Vpp, and 160 Vpp | 85 V, 155 V, and 295 V |
| Pulse Width | Adjustable from 30 ns to 500 ns; resolution of 2.5 ns | Adjustable from 30 ns to 1000 ns (half period of bipolar pulse or duration of negative of pulse); resolution of 5 ns | Adjustable from 30 ns to 1,000 ns; resolution of 2.5 ns |
| Fall Time | < 10 ns | < 10 ns | < 10 ns |
| Pulse Shape | Negative square pulse | Bipolar negative-positive square pulse Negative square pulse | |
| Output Impedance | 28 Ω in pulse-echo 24 Ω in pitch-catch | 35 Ω | < 30 Ω |
| Receiver | PA Channel | – | UT Channels |
| Gain Range | 0 dB to 80 dB maximum input signal; 550 mVp-p (full-screen height). | 0 dB to 80 dB; maximum input signal 900 mVp-p (full-screen height). | 0 dB to 120 dB maximum input signal; 34.5 Vp-p (full-screen height). |
| Input Impedance | 57 Ω ± 10% at 9 MHz in pulse-echo 100 Ω ± 10% at 9 MHz in pitch-catch | 120 Ω ±10 % at 13 MHz | 50 Ω in pulse-echo mode 50 Ω in pulse-receive mode |
| System Bandwith | 0.5 MHz to 18 MHz | 0.2 MHz to 26.5 MHz | 0.25 MHz to 28 MHz |
| Beam Formation | PA Channel | – | UT Channels |
| Scan Type | Single, linear, sectorial, compound, and TFM | – | – |
| Maximum Aperture | OMNIX3-PATFM1664PR = 16 elements OMNIX3-PATFM16128PR = 16 elements OMNIX3-PATFM32128PR = 32 elements | OMNIX3-PATFM64128PR = 64 elements | – |
| Number of Receiving Elements | OMNIX3-PATFM1664PR = 64 receiving elements OMNIX3-PATFM16128PR = 128 receiving elements OMNIX3-PATFM32128PR = 128 receiving elements | OMNIX3-PATFM64128PR =128 elements | – |
| Number of Focal Laws | Up to 1024 | – | – |
| Delay Range Transmission | 0 µs to 10 µs in 2.5 ns increments | 0 µs to 10 µs in 5 ns increments | – |
| Delay Range Reception | 0 µs to 6.4 µs in 2.5 ns increments | – | – |
TFM/FMC
| Supported Modes | Pulse-echo: L-L, T-T, and TT-TT Self-tandem: LL-L, TT-T, TT-L, TL-T, LT-T, TTT-TT, and TL-L |
|---|---|
| Number of Groups | Up to 4 simultaneous TFM groups |
| Maximum Aperture | 64-element aperture for 64:128PR 64-element extended aperture (32:128PR only) 32-element extended aperture for 16:64PR and 16:128PR 128-element extended aperture for 64:128PR |
| Image Resolution | Up to 1024 × 1024 (1 M points) for each TFM group |
| Live TFM Envelope | Yes |
Operating Environment
| Ingress Protection Rating | IP65 certified (completely protected against dust and water jets from all directions (6.3 mm nozzle)) |
|---|---|
| Shockproof Rating | Drop tested according to MIL-STD-810G |
| Intended Use | Indoor and outdoor use |
| Altitude | Up to 2,000 m (6,561 ft) |
| Operating Temperature | −10 °C to 45 °C (14 °F to 113 °F) |
| Storage Temperature | −20 °C to 60 °C (−4 °F to 140 °F) (with battery inside) −20 °C to 70 °C (−4 °F to 158 °F) (with no battery inside) |
